Personalization vs Customization
Overview
Whereas both customization and personalization seek to improve user experience, they operate in a divergent manner. Personalization is based on behavior, dynamically changing content or services depending on user actions and preferences. Customization allows users to take control explicitly to customize features based on their needs. Firms must realize the distinction themselves if they are going to create relevant, interesting, and rewarding experiences without overwhelming or estranging their users.
What is Personalization?
Personalization is the activity of customizing content, experience, or service for a targeted user based on information collected like behavior, preference, or demographics. Personalization works silently in the back end through the use of algorithms and analytics to present a contextual experience without the need for user interaction. From sponsored playlists to hyper-targeted suggestions, personalization leverages real-time data to predict needs so interactions feel smooth, natural, and distinctively personalized.
Benefits of Personalization
- Enhanced Customer Experience
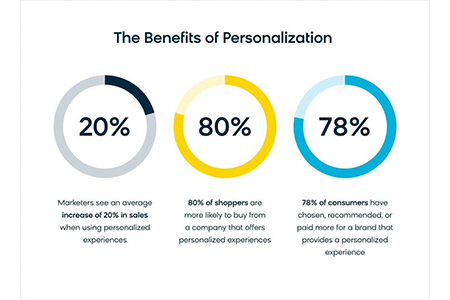
Through its provision of pertinent content and timely suggestion, personalization provides a more natural and engaging experience. Customers are heard, and it increases trust and long-term perception. - Increased Engagement
Individuals will engage more with material or offers that they can explicitly observe are tailored specifically to them. Personalization results in more engagement by making each interaction more pertinent. - Improved Conversion Rates
Experiences that are targeted have better conversion rates. The moment people are presented with what they actually want, they'll take action, buy or subscribe. - Better Customer Loyalty and Retention
When customers feel appreciated through individualized interactions, they'll come back. In the long run, this emotional bond has the possibility to develop into deeper loyalty and retainment for the long term.
Cons of Personalization
- Privacy Concerns
Collecting and handling personal data can potentially trigger alarms over surveillance or exploitation. Businesses must tread carefully and fully meet data privacy regulations. - Data Dependency
In the absence of adequate or right data, personalization is no longer as effective. The nature of the experience relies directly on the accuracy and depth of data gathered. - Complexity and Cost
Personalization involves sophisticated tools, expert teams, and constant optimization. For most companies, it translates into massive initial investment and maintenance expenses. - Risk of Over-Personalization
Overpersonalization is either intrusive or manipulative and will drive the customer away. A blend of relevance and subtlety must be found so that it does not overwhelm the customer.
Types of Personalization
- Rules Based
Rules-based personalization is based on pre-established conditions, like geography or browsing activity, to deliver pertinent content. It's easy, but generally small in scope and inflexible. - Predictive
Predictive personalization uses AI and machine learning to predict what the users require even before they ask for it. It responds in real time, offering greater insight and accurate suggestions.
When to use Personalization?
Personalization rocks when user delight and engagement are the priority, e.g., in content websites, e-commerce, and SaaS. When companies need to remove friction, increase relevance, or inspire certain user behaviors, personalization can be a beast. It's also perfectly aligned to businesses with recurring customer interactions, where behavior data can be used to inform personalized experiences towards improved conversion and retention.

What is Customization?
Customization enables individuals to make products, services, or experiences their own personal preference. Personalization occurs by chance, whereas customization occurs by intention and by individual choice. From the hue of a shoe to the structure of a software dashboard, customization places in the customer's hands the ability to construct something that exactly fits their own distinct needs and desires.

Benefits of Customization
- Greater Customer Satisfaction
Personalization provides customers with control over designing their own experience. With this level of control, they become more emotionally connected and satisfied. - Unique Product Offerings
Giving people the ability to personalize makes one of a kind products or services. This singularity can be a valuable weapon for differentiation within competitive markets. - Stronger Brand Loyalty
When people have some say over what they purchase, they're more interested in what happens as a result, more frequently resulting in longer-term brand allegiance. - Competitive Differentiation
Brands differentiate themselves through customization by providing experiences that are not replicable through mass-market competitors. It's a one-to-one strategy to differentiation in mature markets.
Cons of Customization
- Increased Production Costs
In most cases, customized products tend to require elastic manufacturing or additional support, which is bound to hike costs and hit profitability. - Complexity in Manufacturing
There being numerous permutations of one product can complicate the handling of production processes and supply chains, leading to inefficiencies. - Limited Scalability
It could be challenging to scale customization, particularly where there is human intervention or non-standard production by order. - Longer Delivery Times
Mass producing customized goods is slower to provide, and that could infuriate customers accustomed to instant gratification.
When to use Customization?
Customization works best when customers desire uniqueness, such as with fashion, technology, or luxury goods. It is best applied to niche markets where uniqueness outweighs speed. In B2B environments, customization can be applied to extremely specialized operations or industry needs. Whether a gift-wrapped product offering or a configurable CRM product, customization does its best work in markets where "one-size-fits-all" isn't an option.

Personalization vs Customization
| Feature | Personalization | Customization |
|---|---|---|
| Control | System-driven | User-driven |
| Based On | User data, behavior, AI | User choices and preferences |
| Interaction Level | Passive (automated) | Active (manual input required) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with tech | Limited scalability |
| Flexibility | Reactive to real-time data | Proactive, defined by user |
| Common Use Cases | E-commerce, content platforms, SaaS | Fashion, enterprise software, retail |
| Implementation Effort | High (tech & data required) | Moderate to high (depending on offering) |
| User Experience | Seamless, adaptive | Personal, controlled |
Challenges in implementing Personalization and Customization
Both of these strategies have pitfalls despite the advantages. For personalization, legislation protecting data privacy such as GDPR, the requirement of quality data, and sophisticated tech infrastructure are the main challenges. Customization involves logistics challenges such as stock handling, production intricacy, and longer lead times. Both approaches are also subject to constant monitoring and realigning to shifting customer needs, and therefore strategic planning and resource deployment are essential.
Things to consider for Personalization and Customization
Before choosing either approach, take into consideration your target market, business goals, and production capabilities. Ask yourself if your users value convenience or control. Consider data readiness for personalization, and production flexibility for customization. Look at cost, scalability, privacy compliance, and tech infrastructure. Brand identity alignment and market differentiation should also inform the choice. The best approach finally balances user value against business feasibility.
Applications of Personalization and Customization
These techniques are employed extensively in various industries. User preference recommendations increase sales in online commerce. Online streaming services like Netflix customize content to the audience. In fashion clothing, companies such as Nike provide personalized shoes. In software B2B, Salesforce enables dashboard personalization. Healthcare, finance, and education also see advantages, providing customized services or flexible learning paths to fulfill unique user requirements.
Conclusion
Personalization and customization both provide alternative benefits for modern-day customer experiences. Personalization is data-driven to offer frictionless, relevant content, while customization allows users to create their optimal solutions. The brands that understand when and how to implement these methods can build stronger connections, increase satisfaction, and stay competitive. The opportunity is in careful execution supported by transparent goals and an intimate comprehension of user requirements.



